

4.3电化学(阳极)清洗
Electrochemical (anodic) cleaning
受红锈污染的不锈钢表面的电化学(阳极)清洁基于电抛光的概念。
Electrochemical (anodic) cleaning of stainless steel surfaces contaminated with rouging is based on the concept of electropolishing.
作为电镀过程的相反面,电抛光使用适合的电解液和直流电,以电解金属氧化的方式通过直流电从作为阳极的工件表面去除µm级的材料(金属原子)。
As a reversal of the electroplating process, electropolishing uses a suitable electrolyte and an application of direct current to remove material (metal atoms) on the µm scale from a workpiece surface, which serves as the anode, by means of electrolytic metal oxidation.
电化学去除过程可以成功地和可重复地应用于浸入浴方法和合适的擦拭技术中(作为一个移动版本)。在这些受控电化学处理中,不锈钢腔室的表面质量条件在腐蚀性能和清洁性方面得到了显著改善。
Electrochemical removal processes can be applied successfully and reproducibly in both an immersion bath method and in a suitable wiping technique (as a mobile version). The qualitative surface conditions of stainless steel chambers in terms of corrosion behaviour and cleanability are significantly improved in these controlled electrochemical treatments.
在实际实施任何具体的在线清洁措施之前,设备操作员、设备制造商和电抛光专家的技术人员一起召开工程会议,规划技术、相关安全和组织程序,并讨论必要的准备工作。
Before any specific on-site cleaning measures are actually carried out, the equipment operator, equipment manufacturer and the technicians from the electropolishing specialist come together in an engineering meeting to plan the technical, safety-related and organisational procedure and discuss the necessary preparations.
负责工作安全和卫生的运行方代表也参与准备工作,并由电抛光专家提供必要的数据和信息。
Operator representatives in charge of work safety and hygiene are also involved in the preparations, and are given the necessary data and information by the electropolishing specialist.
由于需要进行的所有工作都需要被提前安装的薄膜外壳完全隔离(见图13),因此该措施可以在不中断MPPU/CSSD操作的情况下在灭菌室上进行,并且使用其他设备可以确保无菌物品的完全持续供应。
Because all of the work that needs to be performed is completely isolated by film enclosures installed ahead of time (see Figure 13), this measure can be carried out on a sterilization chamber without interrupting MPPU/CSSD operations, and a full continued supply of sterile goods can be ensured using the other devices.
电化学清洗包括使用可移动臂式捣固装置结合羊毛状织物物体和嵌入的阴极,和合适的电解液可控地润湿内部表面。在作为阳极的腔室表面的指定工作区域,通过电化学氧化(=电抛光)在受控电阳极/阴极电场中,从表面的材料在5-10µm的范围移除取决于时间的长短。
Electrochemical cleaning involves a controlled wetting of the interior surfaces with a suitable electrolyte using a mobile hand tamping unit in combination with a fleece body and an embedded cathode. In the designated working area of the chamber surface serving as the anode, a time-dependant targeted removal of material from the surface takes place on the scale of 5–10 µm in a controlled electrical anode/cathode field by means of electrochemical oxidation (= electropolishing).
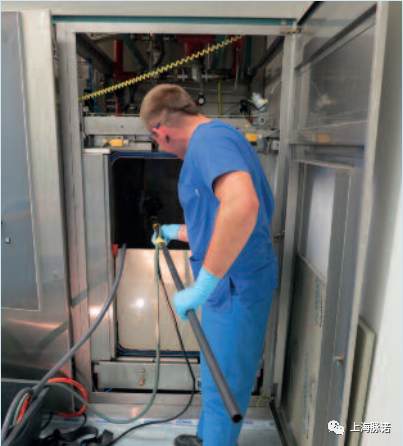

图13a:使用电化学(阳极)清洁对室内表面进行现场修复
On-site rehabilitation of an interior surface on a chamber using electrochemical (anodic) cleaning

图13b:工作空间划分 Workspace partitioning
电抛光过程确保所有的薄层或残留物都被小心地从不锈钢表面去除,而不会留下任何残留物。此外,几乎与目标电化学物质去除的同时,还可以对表面进行微观平整(降低表面粗糙度)。因此,根据材料的特性(原始表面),人们通常可以期望看到表面质量在耐腐蚀性方面的显著改善。
The electropolishing process ensures that all films or residues are carefully removed from the stainless steel surface without leaving behind any residues. In addition, and virtually at the same time as the targeted electrochemical material removal, a micro-smoothing of the surface (reduction of surface roughness) also takes place. As a result of this, and depending on the material characteristics (of the original surface), one can usually expect to see a significant improve- ment in surface quality with regard to corrosion-resistance.

图14:表面轮廓前(深蓝色地形)后(浅蓝色地形)的示意图[4]
Figure 14: Schematic illustration of the surface contour before (dark blue topography) and after (light blue topography) [4]
在应用电化学物质去除和不锈钢表面无残留清洗之后,随后使用符合DIN EN 285(给水)规范的水进行冲洗步骤。在接下来的工作步骤中,通过湿化学钝化的方式建立了钝化层。在最后一步中,用符合DINEN285规范的水(给水)彻底冲洗腔室,并测量电导以监测清洗过程,清洗溶液的所有剩余痕迹都是安全和经验证已去除。
After the applied electrochemical material removal and the resulting residue-free cleaning of the stainless steel surface, a rinsing step is subsequently carried out with water that meets the specifications of DIN EN 285 (feed water). In the work step that then follows, the passive layer is built up by means of wet-chemical passivation. In a final step involving a thorough rinsing of the chamber with water that meets DIN EN 285 specifications (feed water) and the measurement of electrical conductance to monitor the rinsing progress, all remaining traces of the cleaning solution are safely and verifiably removed.
在整个过程中,所有的处理参数,如清洗前后的表面粗糙度、温度、pH和溶液的电导率,都被详细记录下来。一旦设备制造商对设备功能重新认证合格,蒸汽灭菌器可以在大约1-2天的总处理时间后完全交给客户再次使用。
Throughout the entire procedure, all treatment parameters, such as surface roughness before and after cleaning, temperatures, pH and electrical conductance of the solutions, are documented in detail. Once the apparatus has been functionally re-qualified by the equipment manufacturer, the steam sterilizer can be completely handed over to the customer for use again after a total treatment time of approx. 1–2 days.
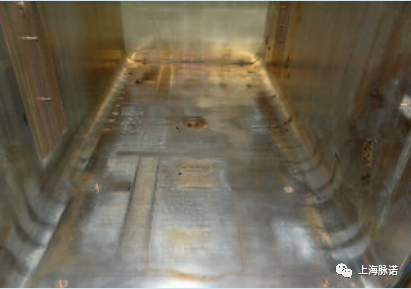
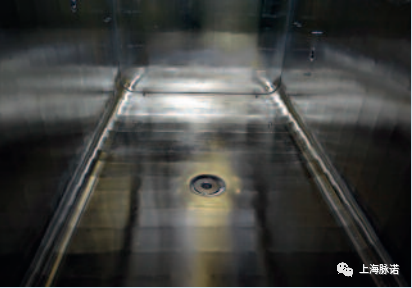
图15a和15b:电化学(阳极)清洗前(左)后(右)的蒸汽灭菌器
Figures 15a and 15b: Steam sterilizer before (left) and after electrochemical (anodic) cleaning (right)
在电化学清洗完成后,腔室的内表面显示出均匀的表面环境,具有显微条件下的平整、反射性/有光泽的特性。此外,在微观范围内进行的表面平整(实际表面积大量减少)导致显著腐蚀性能改善和对未来形成的任何新的膜层和变色的能有更好的易清洁性能。
Following completion of the electrochemical cleaning, the chamber's interior surfaces exhibit homogeneous surface conditions with microscopically smooth, reflective/glossy properties. In addition, the surface smoothing which has taken place on a microscopic scale (massive reduction in actual surface area) results in significantly improved corrosion properties and better cleaning behaviour for any new films and discolourations that form in the future.
电化学清洗也优化和简化了随后的腔室内表面的定期护理。
Electrochemical cleaning also optimises and simplifies the subsequent regular care of a chamber's interior surface.
来自:德国的钱伯斯工作组(德语缩写:AKK)的手册

售前咨询热线:
郑女士:19916799140
(微信同号)
设备销售部:
邓经理:18017268222
张女士:17317169140(小型设备类)
王经理:15921887786
加工事业部(金山工厂):
张经理:18001952488
许先生:19921860084
胡经理:19370589140

企业地址:
上海市金山区朱泾镇朱泾工业园区新顺路8号

企业邮箱:
sales@mirrorglabrous.com